The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in 2017 significantly transformed India’s taxation framework. For businesses operating in the country, understanding GST filing obligations is crucial for compliance and the avoidance of penalties. This detailed guide offers all the necessary information regarding GST filing and the processes, deadlines, and best practices related to GST return submissions.
What is GST Filing?
GST filing refers to the process of submitting various tax returns to the government authorities under the Goods and Services Tax framework. Every registered taxpayer under GST is required to file returns periodically that outline their sales, purchases, tax collected, and tax paid. This process enhances transparency within the tax system, allowing the government to monitor business activities nationwide.
The GST filing system supports a smooth flow of input tax credits and keeps an extensive record of all business transactions. Businesses are required to submit these returns electronically via the GST portal, improving efficiency and minimizing paperwork compared to the previous taxation system.
Understanding GST Return Filing
GST return filing refers to the process of submitting necessary GST returns within set deadlines. These returns detail a business’s taxable sales, claims for input tax credits, and tax obligations for a specific timeframe. The type and frequency of returns depend on the business’s nature, turnover, and registration category.
The GST return filing system is based on self-assessment, which means it is the taxpayer’s responsibility to determine their tax obligations and file accurate returns. This system highlights the importance of maintaining proper accounting records and adhering to GST regulations.
Types of GST Returns and Filing Requirements
It is essential to understand the various types of GST returns for compliance. The table below summarizes the key categories of GST returns
| Return Type | Description | Who Must File | Filing Frequency |
| GSTR-1 | Details of outward supplies | All regular taxpayers | Monthly/Quarterly |
| GSTR-2A | Auto-populated purchase details | All registered taxpayers | Monthly |
| GSTR-2B | Static auto-draft of ITC | All registered taxpayers | Monthly |
| GSTR-3B | Summary return with tax payment | Regular taxpayers | Monthly |
| GSTR-4 | Return for composition dealers | Composition scheme taxpayers | Quarterly |
| GSTR-5 | Return for non-resident taxpayers | Non-resident taxpayers | Monthly |
| GSTR-6 | Return for input service distributors | Input service distributors | Monthly |
| GSTR-7 | Return for tax deducted at source | TDS deductors | Monthly |
| GSTR-8 | Return for tax collected at source | E-commerce operators | Monthly |
| GSTR-9 | Annual return | All regular taxpayers | Annually |
| GSTR-10 | Final return | Taxpayers surrendering registration | One-time |
Monthly GST Filing Process: Step-by-Step Guide
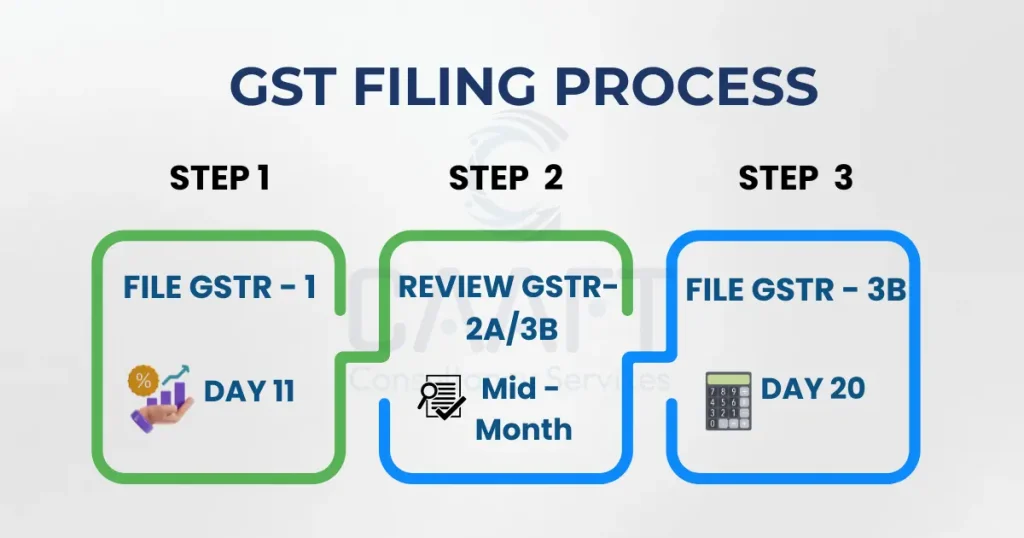
The monthly GST filing process generally includes submitting GSTR-1, reviewing GSTR-2A/2B, and filing GSTR-3B. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the process:
Step 1: Prepare and Submit GSTR-1
GSTR-1 includes information on all outward supplies made during the month. Taxpayers must accurately report detailed sales information, including the GSTIN of recipients, invoice numbers, dates, and tax amounts. This return needs to be filed by the 11th of the subsequent month for monthly filers, while the deadlines differ for quarterly filers.
Step 2: Examine GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B
GSTR-2A is automatically populated based on the GSTR-1 filings of suppliers, while GSTR-2B provides a static view of available input tax credit. Taxpayers should frequently review these returns to confirm that all eligible credits are available and resolve any discrepancies with their purchase records.
Step 3: Submit GSTR-3B with Tax Payment
GSTR-3B functions as a summary return in which taxpayers report their total outward supplies, claim input tax credits, calculate their net tax liability, and make payment. This return must be submitted by the 20th of the following month, and any taxes owed must be paid before filing.
Key Deadlines for GST Return Filing
Timely filing of GST returns is crucial to avoid late fees and penalties. The following table summarizes the key deadlines:
| Return Type | Monthly Filers Due Date | Quarterly Filers Due Date | Annual Return Due Date |
| GSTR-1 | 11th of next month | 13th of next month, after the quarter | N/A |
| GSTR-3B | 20th of next month | 24th of next month, after the quarter | N/A |
| GSTR-4 | N/A | 18th of next month, after the quarter | N/A |
| GSTR-9 | N/A | N/A | December 31st of the next financial year |
| GSTR-9C | N/A | N/A | December 31st of the next financial year |
Input Tax Credit and GST Filing
Input Tax Credit (ITC) enables businesses to receive a credit for taxes paid on inputs utilized in their operations. Accurate GST return submissions allow businesses to claim qualifying ITC and keep precise records. The ITC claiming process is closely tied to the supplier’s GSTR-1 filing, as the credit is recorded in the recipient’s GSTR-2A only after the supplier submits their details on outward supplies.
Businesses should keep meticulous records of all input purchases and consistently reconcile their accounts with GSTR-2A to optimize ITC benefits. They must promptly address any inconsistencies with suppliers to ensure corrections in future filings. If a supplier fails to file returns or cancels their registration, the ITC that has been claimed must be reversed.
Common Challenges in GST Filing and Solutions
Data Management and Record Keeping
Keeping accurate and thorough records of all transactions is a significant challenge for businesses. Adopting reliable accounting software that integrates with GST filings can greatly minimize mistakes and streamline operations. Regularly backing up data and retaining physical copies of essential documents is critical.
Reconciliation Issues
Discrepancies between financial records and GST returns, particularly in reconciling GSTR-2A, are prevalent. Businesses should implement monthly reconciliation routines and maintain open lines of communication with suppliers to swiftly resolve any discrepancies. Utilizing reconciliation software can automate much of this task.
Technical Difficulties
The GST portal may encounter technical problems, especially during high filing seasons. Businesses should refrain from waiting until the last minute to file and allow extra time before deadlines. Having alternative internet access and readily available technical support can help navigate these challenges.
Penalties and Compliance Requirements
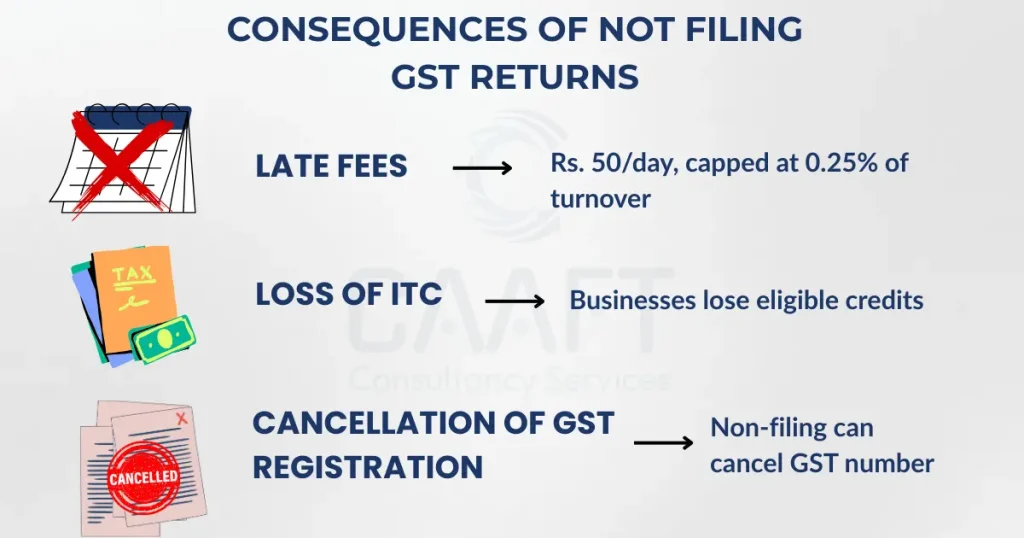
Failure to adhere to GST filing obligations results in various penalties and repercussions. Late returns incur a fee of ₹50 per day for each return (CGST + SGST), capped at 0.25% of total turnover. Not filing returns can lead to the cancellation of GST registration and loss of input tax credits.
The government has implemented several compliance measures, such as e-invoicing for enterprises with turnover over designated thresholds, which directly influences the GST filing process. Businesses must remain informed about evolving compliance regulations and ensure their systems can accommodate new requirements.
“Avoid penalties & save time — Get expert GST filing support from CAAFT“
Optimizing GST Filing Practices
Implementing systematic strategies for GST filing can greatly improve compliance and reduce expenses. Companies should develop precise monthly calendars that emphasize all essential GST deadlines and dates. Continuous training for accounting personnel regarding GST updates and changes facilitates better compliance. Utilizing GST-compliant accounting software for automation helps eliminate manual mistakes and conserves time. Performing routine internal audits is beneficial for spotting and addressing problems before they escalate into compliance issues. Keeping organized documentation and approval workflows for all transactions guarantees accuracy in submissions.
The Impact of Technology on GST Filing
The advancement of technology in GST filing has introduced various digital solutions that make compliance easier and increase efficiency.
- Cloud-based accounting systems provide immediate access to financial information and automate GST calculations, streamlining the process.
- API connections with the GST portal enable businesses to transfer data straight from their accounting software, thereby significantly decreasing manual data entry mistakes.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications have become essential for GST reconciliation, as they uncover data discrepancies, pinpoint errors, and even recommend corrections.
These technological advancements not only conserve time but also improve the accuracy of the filing process.
Ongoing Updates in the GST Framework
The government consistently enhances the GST system by rolling out new features and simplifications to provide a better filing experience for taxpayers and enhance compliance.
- The expansion of e-invoicing will soon introduce greater consistency and transparency to the system.
- Improved return forms will ease the reporting process and make it more intuitive.
- Better integration across various modules promises enhanced collaboration among different components of the GST framework.
These changes indicate a move towards a more efficient and technology-focused tax environment.
Preparing for Upcoming Changes
Businesses should proactively gear up for these alterations by implementing flexible compliance strategies.
- Invest in versatile technology that can readily adapt to ongoing changes.
- Stay updated through tax professionals to ensure alignment with evolving regulations.
- Engage in GST training sessions to improve compliance preparedness.
By merging technological adoption with continuous education, businesses can assuredly navigate the future of GST filing.
Conclusion
GST filing and return submissions are essential aspects of regulatory compliance for businesses in India. Effectively handling these responsibilities relies on recognizing the different types of returns, keeping precise records, and adhering to structured procedures. Through careful preparation, technology use, and expert advice, businesses can effectively handle their GST compliance while concentrating on their primary activities.
The secret to effective GST filing is to view it as a vital component of business functions instead of a compliance hassle. By adopting best practices, utilizing technology, and remaining informed about changes in regulations, businesses can achieve seamless GST compliance while optimizing their input tax credit advantages and maintaining a positive relationship with tax authorities.



